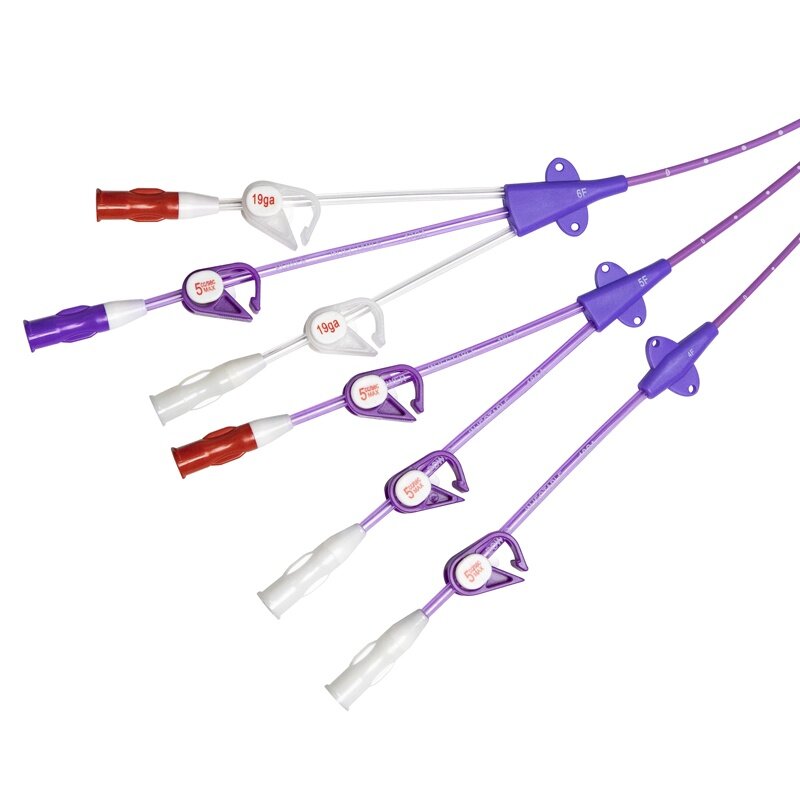
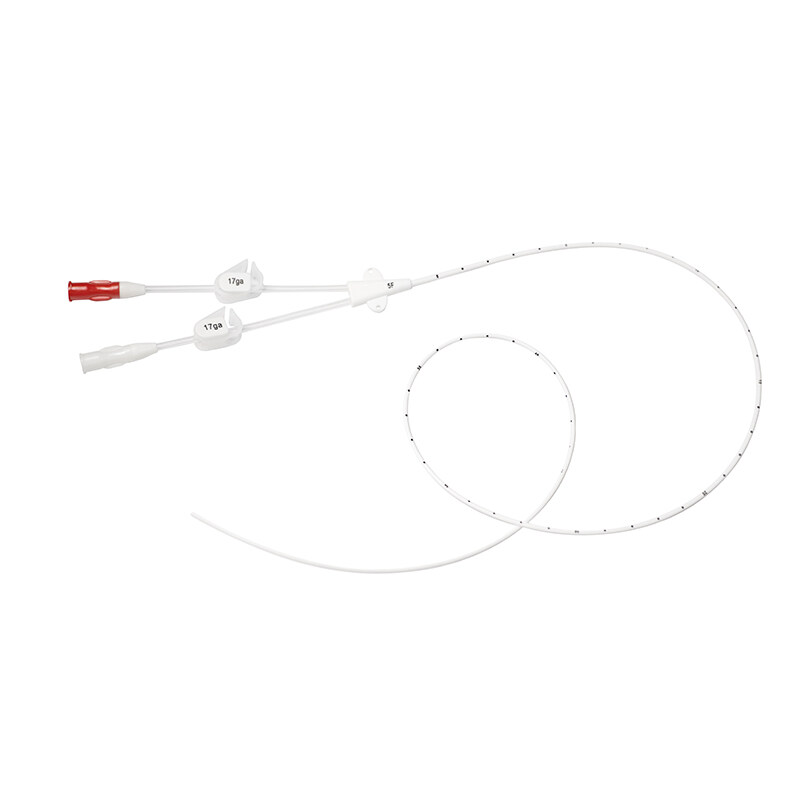
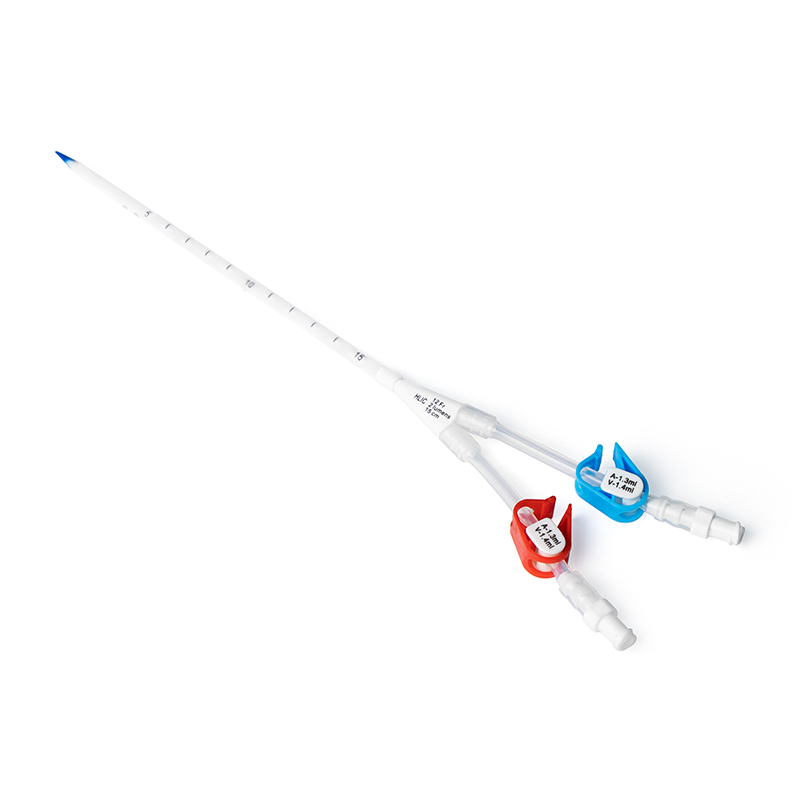
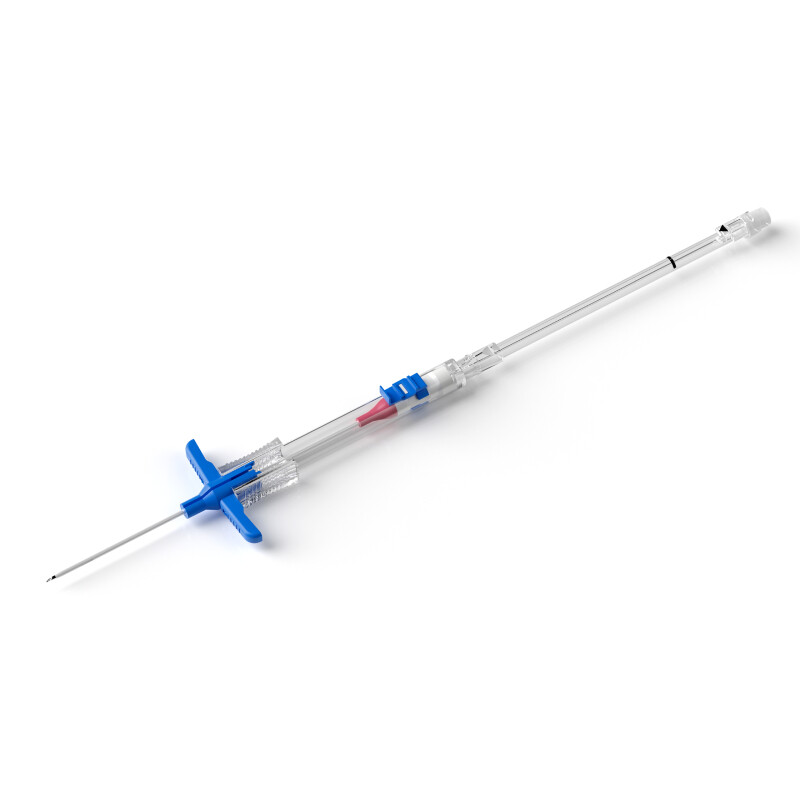
Hemodialysis is a life-saving procedure for individuals with kidney disease. A hemodialysis catheter is a flexible, hollow tube that is inserted into a vein, usually in the neck, or chest. During hemodialysis, blood is removed from the body, filtered, and then returned to the body through a hemodialysis catheter.
Features of Hemodialysis Catheter Kit
● Smooth tube surfaces reduce the adhesion of platelets and minimize the risk of thrombosis.
● Enhanced polyester CUFF to secure the catheter and reduce the rate of infection.
● Staggered side hole design to reduce the risk of blood recycling.
● Advanced medical polyurethane materials
Polyurethane is thermosensitive and can be softened after insertion.
Antibacterial and will not be damaged by microbial attacks.
● Rotatable suture wing provides safety and comfort with external anchoring.
● One -piece-shaped tip is soft and flexible, minimizing the risk of vessel wall trauma and phlebitis.
● The catheter is radio-opaque that could be visualized under chest X-ray for easy positioning control.
● Curved extensions for improved comfort and patient care.
● ID-clamps designed for indicating priming volume and simplifying the identification of arterial and venous lumen.
● Large side holes and double D profile design to provide greater flow rates at lower pressure and minimize the risk of clotting.

Nursing After Hemodialysis Catheter Insertion
Proper care of the hemodialysis catheter is essential to prevent infections and ensure the success of the hemodialysis treatment. Here are some hemodialysis catheter care guidelines:
● Follow the healthcare provider's instructions
The healthcare provider will provide you with specific instructions for caring for your hemodialysis catheter. Follow these instructions carefully to ensure the success of your treatment and prevent infections.
● Keep clean and dry and Keep the catheter away from water
It is important to keep the area around the catheter clean and dry. Use soap and water to clean the area before and after touching the catheter. Use a clean, dry towel to dry the area.
● Avoid touching the catheter
Avoid touching the catheter as much as possible. This can introduce bacteria into the catheter, which can cause a hemodialysis catheter exit site infection. If you must touch the catheter, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water first.
● Keep the catheter covered
Cover the catheter with a sterile hemodialysis catheter dressing to protect it from dirt and bacteria. Change the hemodialysis catheter dressing as directed by your healthcare provider.
● Do not use the catheter for anything else
The catheter is only for hemodialysis. Do not use it to draw blood, give medications, or for any other purpose.
● Avoid using any lotions or creams near the catheter insertion site
Using lotions or creams near the insertion site can increase the risk of infection. Therefore, it is best to avoid using any lotions or creams in that area.
● Do not pull or tug on the catheter
Pulling or tugging on the catheter can cause it to dislodge or damage the insertion site.
● Monitor the site for signs of infection
By following these precautions, you can help ensure the longevity of your hemodialysis catheter and reduce the risk of infection. Remember to work closely with your doctor or nurse to address any concerns or questions you may have regarding your catheter care.