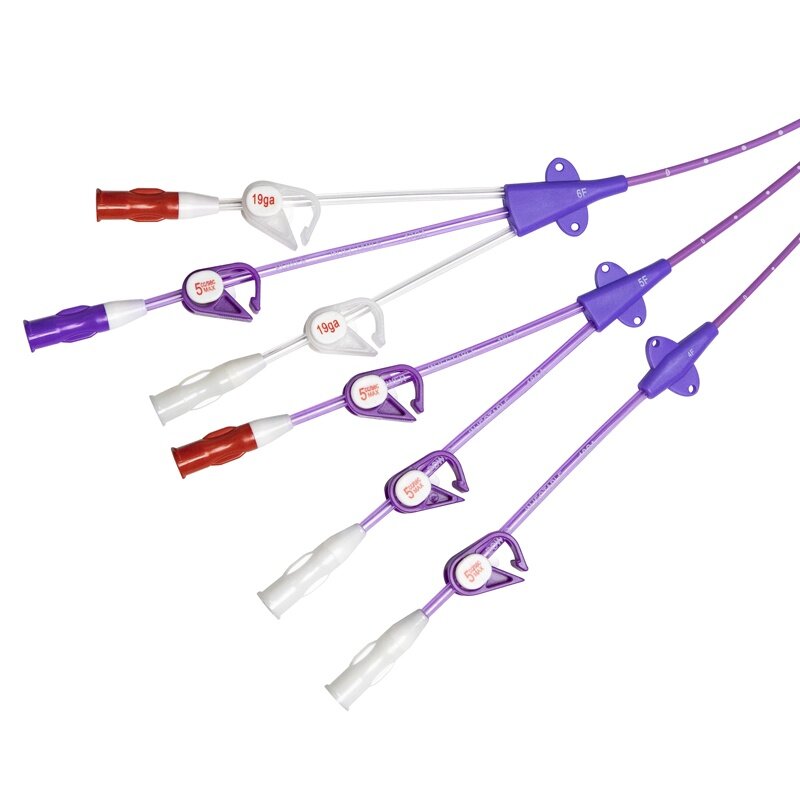
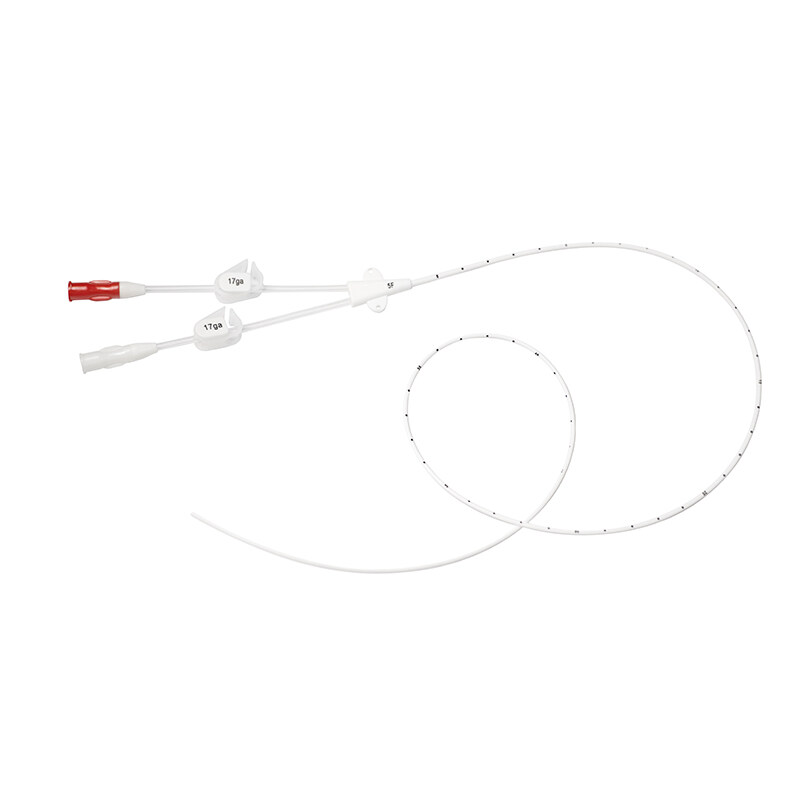
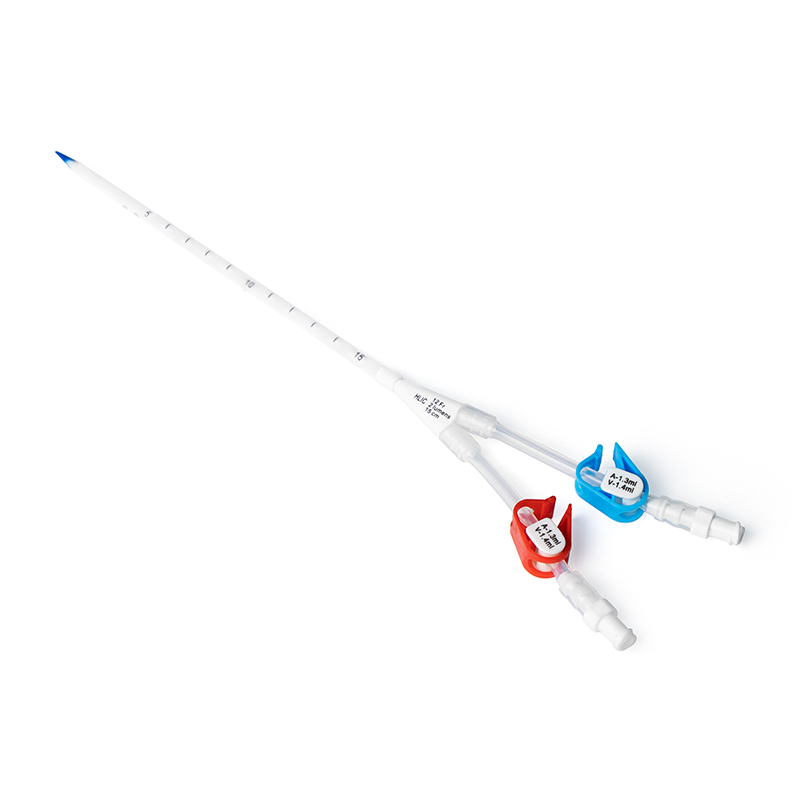
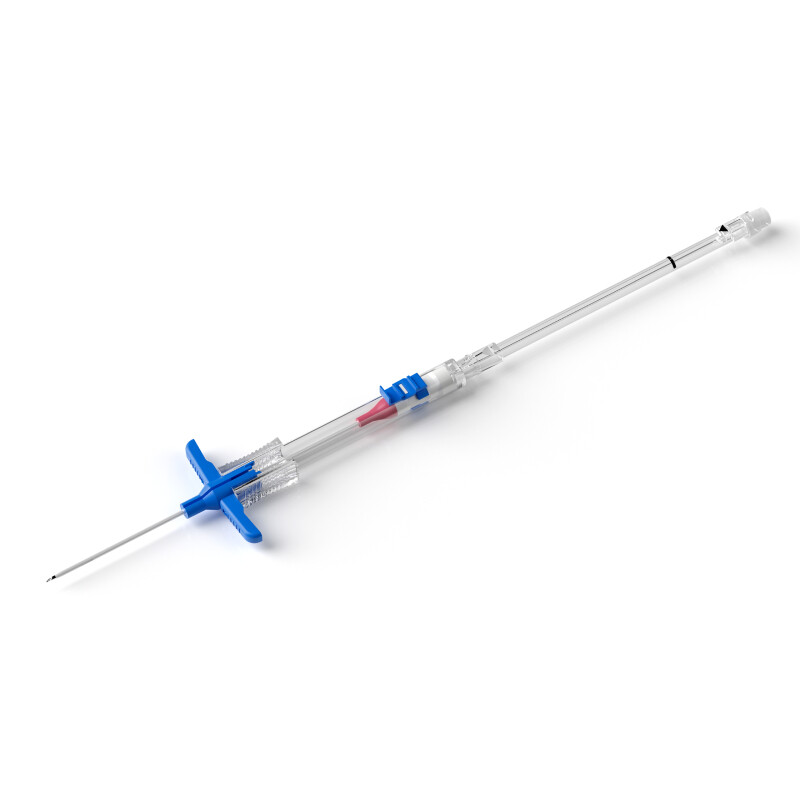
Blockage of hemodialysis catheters can sometimes occur, which can affect the effectiveness of treatment. Understanding a hemodialysis catheter blockage and how to manage it is important to a patient's hemodialysis process.
Stop the treatment
The first thing to do when a hemodialysis catheter is clogged is to stop the treatment immediately. Continuing the treatment can increase the risk of complications, such as infection, bleeding, or damage to the catheter.
Assess the catheter
The next step is to assess the catheter to determine the cause of the blockage. Blockages can be caused by blood clots, fibrin sheaths, or other factors. In some cases, the catheter may need to be removed and replaced.
Try to flush the catheter
If the blockage is not severe, the healthcare provider may try to flush the catheter with a saline solution or other medication to clear the blockage. This process is known as catheter clearance or decluttering.
The doctor or nurse may use a specialized device, such as a catheter lock or thrombolytic agent, to help clear the blockage.
Use other interventions
If flushing the catheter does not work, other interventions may be necessary. These may include using a guidewire or balloon catheter to remove the blockage or using a surgical procedure to remove the blockage.
Monitor for symptoms
Even after the catheter has been cleared, it is important to monitor for any symptoms that may indicate a problem, such as redness or swelling at the insertion site, fever, or chills.
Practice good hygiene
Practicing good hygiene is important to prevent infections and other complications. This includes washing your hands frequently, keeping the catheter insertion site clean and dry, and avoiding touching the catheter unless absolutely necessary.
Follow your treatment plan
Finally, it is important to follow the treatment plan as prescribed by a doctor. This includes attending all scheduled hemodialysis treatments, taking medications as prescribed, and following any other recommendations for managing your condition.

Prevent future blockages
Once the blockage has been cleared, it is important to take steps to prevent future blockages. This may include maintaining good hygiene at the catheter insertion site, using anticoagulant medications as prescribed by the healthcare provider, and avoiding activities that may increase the risk of clotting, such as smoking or sitting for long periods of time.
A clogged hemodialysis catheter can interfere with the effectiveness of hemodialysis treatments and increase the risk of complications.
By following these steps and working closely with the doctor, patients can help to prevent future blockages and ensure that their hemodialysis treatments are as effective as possible.