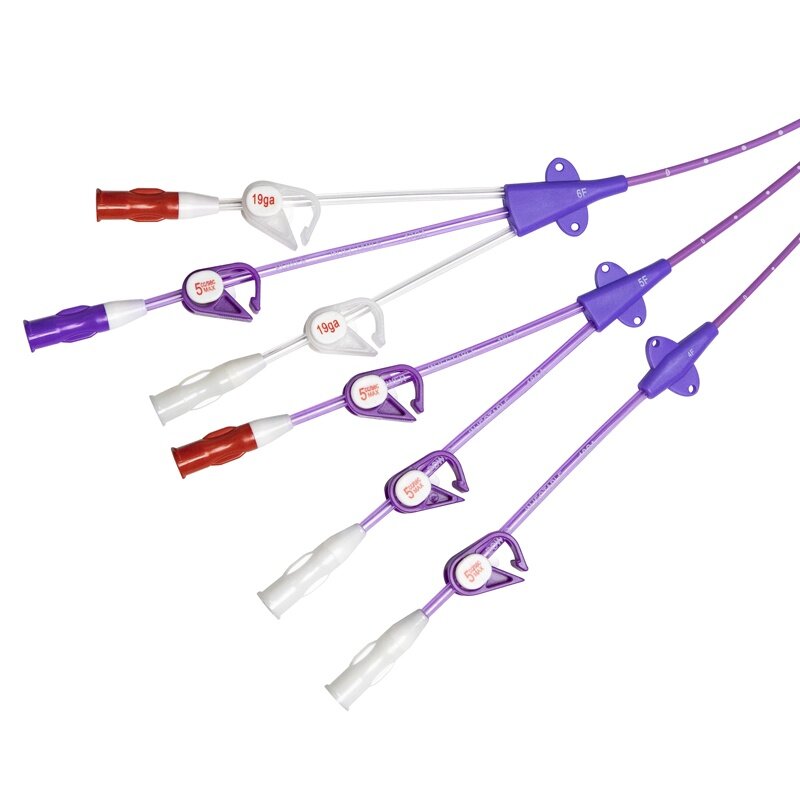
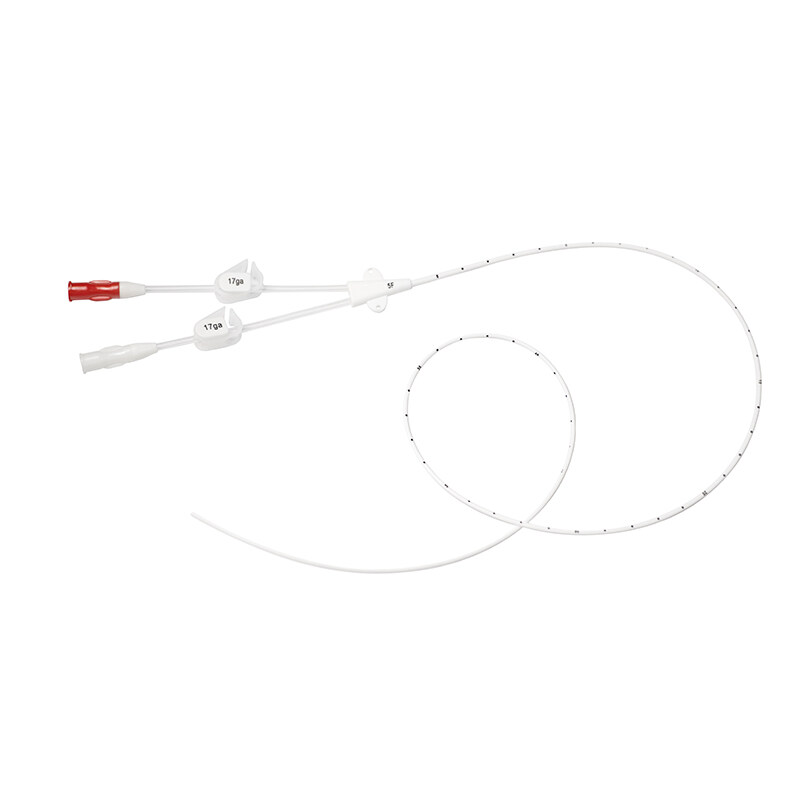
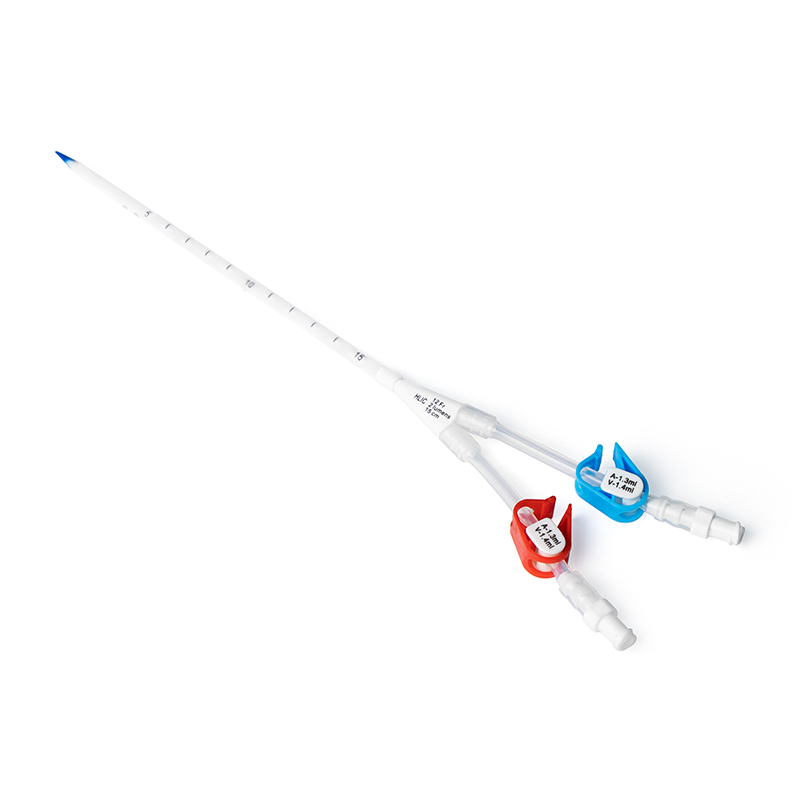
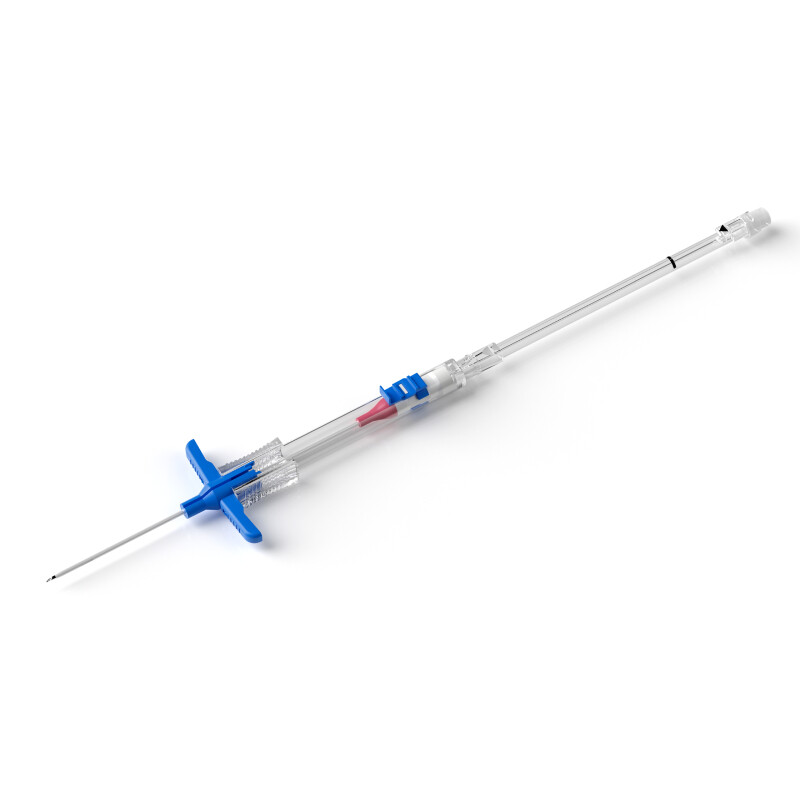
Central Venous Catheter Devices
A central venous catheter (CVC) is a type of catheter that is inserted into a large vein in the body, usually in the neck, chest, or groin.
Central venous catheter devices include all the necessary components to insert and use the catheter safely and effectively.
Central venous catheterization kit is used to provide long-term access to the bloodstream for a variety of medical treatments, including administering medications, fluids, and nutrition, as well as monitoring blood pressure and taking blood samples.
Components of Central Venous Catheter Devices
A central venous catheterization kit typically includes several components, including:
Catheter: The catheter itself is a flexible, hollow tube that is inserted into a vein and secured in place. It can vary in length and diameter, depending on the patient's needs.
Introducer needle: A needle that is used to puncture the skin and enter the vein, creating a pathway for the catheter to be inserted.
Guidewire: A thin, flexible wire that is inserted through the introducer needle and into the vein. The catheter is then threaded over the guide wire and into the vein.
Dilator: A blunt instrument that is used to widen the puncture site and create a larger opening for the catheter to be inserted.
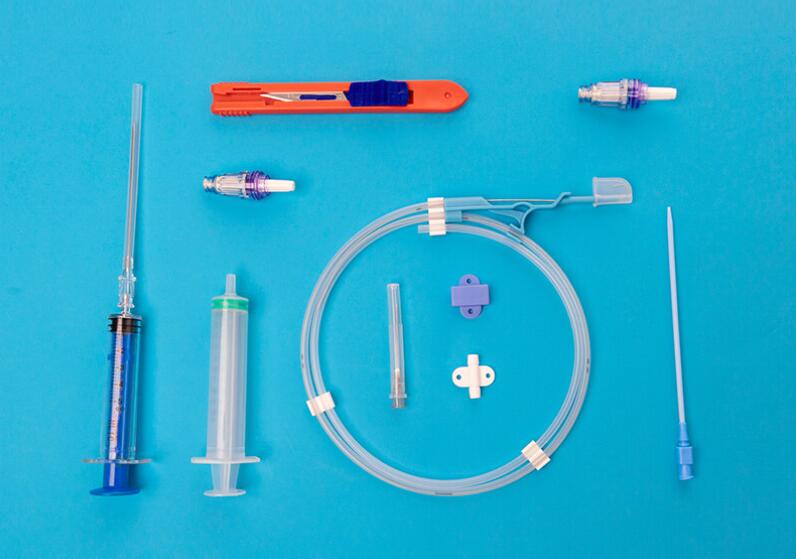
Central Venous Catheter Devices
Why Use Central Venous Catheter Devices?
The catheter can remain in place for weeks or even months, unlike other types of catheters that need to be replaced more frequently.
A central venous catheter is also used when it is necessary to administer medications or other fluids that are irritating to the veins, as the catheter is inserted into a larger vein that can handle a greater volume of fluid.
In addition, a central venous catheter is often used when a patient's veins are difficult to access, such as in patients with chronic illnesses or those undergoing chemotherapy.
Uses of a Central Venous Catheterization Kit
Central venous catheter devices have many uses in healthcare, including:
Hemodialysis: Patients with kidney failure may require hemodialysis, which involves removing blood from the body, filtering it through a machine, and returning it to the body. Central venous catheter devices can provide access to the bloodstream for hemodialysis treatments.
Chemotherapy: Patients undergoing chemotherapy often require frequent access to their bloodstream to receive medications. Central venous catheter devices can provide this access, allowing chemotherapy drugs to be delivered safely and effectively.
Parenteral nutrition: Patients who are unable to eat or digest food normally may require parenteral nutrition, which is delivered directly into the bloodstream. Central venous catheter devices can provide long-term access to the bloodstream, making it easier to administer parenteral nutrition.
Monitoring: Central venous catheter devices can also be used to monitor blood pressure and take blood samples, making them useful in critical care settings.
To minimize the risks of central venous catheter infection, it is important that a central venous catheterization kit is only used by trained healthcare professionals who follow strict guidelines for insertion, maintenance, and removal of the catheter.

Conclusion
Central venous catheter devices are useful tools in healthcare settings, providing long-term access to the bloodstream for a variety of medical treatments.
It is important to note that the catheter is only inserted by trained healthcare professionals who follow strict guidelines for use and maintenance.
Overall, the benefits of central venous catheter kits outweigh the risks for many patients. By using a central venous catheter kit safely and effectively, healthcare providers can improve the care and outcomes of their patients. It means that they can be used for a longer period of time, reducing the need for multiple needle sticks and reducing discomfort for patients.